Bordered by China to the north and the Gulf of Thailand to the south, Vietnam is home to a rich culture and history, with major influences from countries such as Laos and Cambodia. The country is known for its brilliant coastline that spreads across 3,400 kilometers, along with its beautiful mountains, rivers, and rainforests. Vietnam is also one of the most popular tourist destinations in the world, featuring world heritage sites such as Ha Long Bay and cities such as Hanoi with French colonial architecture.
Vietnam is also a rapidly developing country with a young population and a growing economy. The country is primarily dependent on its services sector, accounting for over 50 per cent of its GDP (Gross Domestic Product), followed by the industrial and agricultural sectors. It should also be known that Vietnam’s economy also relies largely on FDIs (Foreign Direct Investments), to continually support its economic growth. And by 2050, the country is slated to be the 10th largest economy in the world. Having said that, if a visit to Vietnam is on your cards and therefore have applied for a visa, then it is essential that you check its current status by following our step-by-step guide.
How to Check Visa Status Online
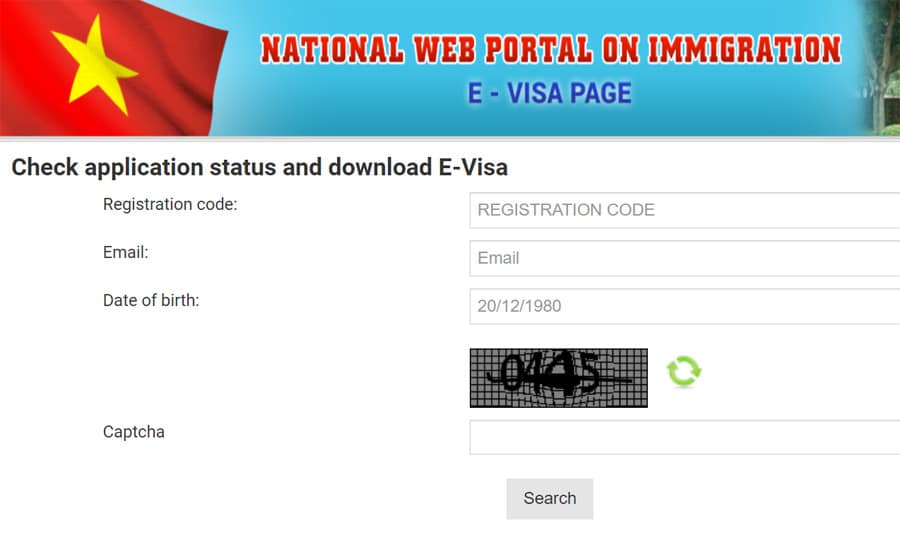
The Vietnamese Government has created a national web portal through which travelers can apply for an e-visa (electronic visa), issued by the Vietnamese Immigration Department. The e-visa will be valid for a maximum of 90 days and can be applied for either single or multiple entries. However, there are certain conditions that the applicant needs to fulfill to be able to apply for them. These include holding a valid passport and not being suspended from entry/exit/transit/holding residence in Vietnam.
To apply for an e-visa, applicants are required to provide their personal information (such as name, date of birth, gender, etc.) and upload a scanned copy of their passport data page along with a scanned photograph (looking straight without glasses). Once done, the fee for the application must be paid, which is $25 for a single entry or $50 for a multiple entry. After successfully making the payment, your e-visa will be processed within three working days. To check your current e-visa status, follow the suggested steps mentioned below.
- Start the visa status-checking process by heading over to the official website here.
- On the landing page, enter the registration code (that was emailed to you during the application process), your email address, and your date of birth. After that, click on “Search”.
- Your current e-visa status will then be shown on your screen.
How to Contact For Help
The best possible way to get in touch with the Vietnamese Immigration Department for your e-visa is via the online contact form here.
Simply enter your name, passport number, nationality, registration email, the type of problem you are facing, and an overall description of your issue. Once done, click on “Send,” and the relevant visa authorities will get in touch with you within the next few working days.
Overview of Visas

When traveling to Vietnam, applying for a visa to enter the country is a crucial task that you must complete. But, to ensure that you are applying for the correct visa type, it is also important that you obtain a thorough idea of the legal scenario. The Vietnamese Immigration Department has introduced a variety of visa types, all of which have been explained below.
Tourist Visa: Tourist visas are issued to passengers who are traveling to Vietnam only for tourism purposes and not performing any business-related activities. Tourist visas can be single-entry or multiple-entry, with a maximum validity of three months.
Business Visa: Business visas offered by Vietnam can be of two types, namely, DN1 and DN2. The DN1 visa is provided to foreigners who work with other organizations and businesses having legal status in the country. On the other hand, DN2 visas are issued to foreigners who plan to arrive in the country to establish a commercial presence or perform any other activity backed by international treaties, of which Vietnam is a member. Business visas can also be single or multiple entry, with a maximum validity of three months.
Student Visa: Student visas are granted to those who are planning to attend a university course in Vietnam. This type of visa can be applied for after reaching Vietnam with the help of a tourist visa. And once you enroll in your preferred course, the tourist visa can be swapped with a student visa.
Working Visa: Foreigners who are willing to come to Vietnam (along with a work permit or a work-permit-free written confirmation) with the intention of working in the country, such as a teacher or any other profession, would be allowed to opt for a working visa. Working visas usually carry a maximum validity of two years, after which, if you want to extend your stay, you have to apply for a temporary residence card, which will be valid for another two years.
Investor Visa: Foreign investors who are looking to invest in a business in Vietnam are provided with investor visas. Additionally, investor visas are of four types, namely – DT1, DT2, DT3, and DT4. DT1 is issued to investors who are looking to invest at least VND100 billion, while the DT2 visa is provided to those who are planning to invest between VND50 and VND100 billion. Both visas are valid for up to five years. On the other hand, DT3 is issued to investors looking to invest between VND3 and VND50 billion with a validity of three years, and DT4 is for investors who are planning to contribute less than VND3 billion with a validity of up to 12 months.
Diplomatic Visa: Foreigners who are members of a delegation, consulate personnel, or those who are working for either of the aforementioned members are provided with a diplomatic visa. There is no fee involved when applying for a diplomatic visa since the decision will be made by the applicant’s home country and the Vietnamese Embassy. Also, this visa carries a maximum validity of 12 months.

